Frijoles: History, Varieties, Health Benefits, and Creative Recipes
Beans, commonly referred to as frijoles, have origins tracing back to ancient Latin America. Archaeological evidence points to domestication over 7,000 years ago. Civilizations such as the Maya and Aztec cultivated beans alongside corn and squash, forming a staple trio of crops. Frijoles integrated into daily diets, often taking center stage in meals. They were not just food but a necessary component of survival and culture.
Cultural Significance Through the Ages
Frijoles maintained their cultural significance as societies evolved. During the colonial era, beans became critical in Spanish cuisine after being introduced to Europe. They featured prominently in traditional dishes like feijoada in Brazil and refried beans in Mexico. Beans also played a role in religious and ceremonial contexts. Their ability to be stored and consumed during droughts further cemented their importance.
Throughout history, frijoles have symbolized sustenance and resilience. They remain a beloved ingredient across Latin America, embodying a rich culinary heritage.
Types of Frijoles: Varieties Worth Knowing
Common Differences Between Black, Pinto, and Red Beans
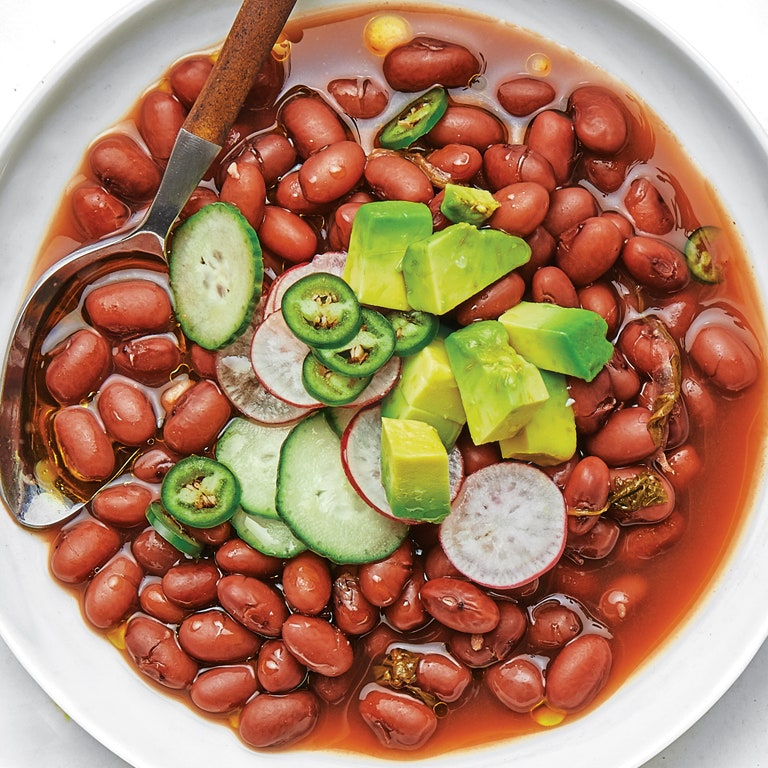
Black beans, pinto beans, and red beans each offer unique flavors and culinary uses. Black beans, often integral to Caribbean and Latin American dishes, have a dense, meaty texture. Rich in antioxidants, they’re known for their slightly sweet flavor. Pinto beans, a staple in Mexican cuisine, are easily recognizable by their mottled skin. When cooked, they become creamy and slightly earthy, making them perfect for refried beans. Red beans, commonly used in Cajun and Creole cuisine, have a smooth texture and a slightly nutty taste. They stand out in dishes like red beans and rice.
Regional Varieties and Their Unique Characteristics
Different regions have cultivated varieties of frijoles with unique characteristics. In Mexico, the Flor de Junio beans are notable for their pink color and tender texture, prized in soups and stews. Central America offers the small red Salvadoran beans, known for their strong flavor and ability to retain their shape in cooking. Peru introduces the Peruano beans, yellow and buttery, ideal for creamy dishes. In Spain, the Judion beans, large and white, are used in traditional stews like Fabada Asturiana. Each variety reflects the local climate and culinary traditions.
Cooking With Frijoles: Best Practices
Preparing Beans for Cooking
To ensure frijoles are ready for cooking, start with dried beans and rinse them thoroughly to remove dirt and debris. Inspect beans for any stones or damaged beans and discard them. Soaking beans can reduce cooking time and ensure even texture; soak them overnight in three times their volume of water. If you’re short on time, a quick soak method involves boiling beans for 2 minutes, then letting them sit covered for 1 hour. For canned beans, drain and rinse them under cold water to remove excess sodium and preservatives.
Tips for Achieving Perfect Texture
Achieving the perfect texture for frijoles hinges on cooking method and time. Use a heavy-bottomed pot or Dutch oven to distribute heat evenly. After bringing beans to a boil, reduce heat to a simmer to prevent splitting. Add salt toward the end of cooking to avoid toughening the beans. Monitor beans for doneness by testing a few; they should be tender but not mushy. If using a pressure cooker or slow cooker, adjust times accordingly: around 20-30 minutes for a pressure cooker and 6-8 hours on low for a slow cooker. Avoid adding acidic ingredients like tomatoes or vinegar before beans soften, as they can inhibit the cooking process.
Health Benefits of Frijoles
Nutritional Profile of Frijoles
Frijoles, or beans, present a rich nutritional profile, making them a valuable addition to your diet. A one-cup serving of cooked beans provides approximately:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Protein | 15 grams |
| Fiber | 15 grams |
| Iron | 15% of DV |
| Folate | 50% of DV |
| Magnesium | 20% of DV |
| Potassium | 15% of DV |
These nutrients offer several health benefits. Protein supports muscle repair and growth. Fiber aids in digestive health and promotes satiety. Iron helps maintain healthy blood cells. Folate plays a role in DNA synthesis and repair. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure.
Frijoles in Dietary Recommendations
Health organizations like the American Heart Association and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend including beans in your diet. These recommendations focus on the various health benefits associated with frijoles:
- Heart Health: The fiber, potassium, and folate in beans contribute to cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol levels and regulating blood pressure.
- Digestive Health: High fiber content supports bowel regularity and reduces the risk of digestive diseases.
- Weight Management: Beans’ protein and fiber content enhance feelings of fullness, aiding in weight management and obesity prevention.
Incorporating frijoles into your meals is straightforward. Add them to salads, soups, stews, or serve them as a side dish. This versatility ensures you can enjoy beans in various forms while benefiting from their rich nutritional profile.
Frijoles in Modern Cuisine
Fusion Dishes That Include Frijoles
Fusion dishes creatively integrate frijoles with other culinary traditions. Korean-Mexican tacos combine Korean BBQ flavors with refried beans and kimchi. Frijoles negros pair with Mediterranean staples like hummus and pita, creating a unique fusion. Indian-Mexican burritos feature black beans, paneer, and curry spices, blending rich flavors from both cuisines. Chefs globally experiment with such combinations to craft innovative dishes.
Frijoles as a Staple in Vegan and Vegetarian Diets
Frijoles are a cornerstone in vegan and vegetarian diets due to their high protein content. Black beans form the base of vegan chili, providing essential amino acids. Pinto beans star in vegetarian burrito bowls, delivering protein and fiber. Lentil and frijoles burgers offer a plant-based alternative to meat patties. Including frijoles in meals ensures balanced nutrition without animal products. Health-conscious individuals frequently incorporate frijoles to meet dietary protein needs.
Conclusion
Frijoles are more than just a culinary staple; they’re a cultural icon and a nutritional powerhouse. Whether you’re enjoying traditional dishes or exploring innovative fusion cuisine, beans offer versatility and health benefits that are hard to beat. Their significant role in vegan and vegetarian diets also makes them essential for anyone looking to maintain a balanced, protein-rich diet. By incorporating frijoles into your meals, you’re not only honoring a rich history but also making a healthy and delicious choice for your culinary adventures.